LR44 and 357 batteries are widely used in various electronic devices, offering distinct characteristics to meet specific application requirements. Both batteries share similar dimensions, with a diameter of approximately 11.6 mm (0.457 inches) and a height of around 5.4 mm (0.213 inches).

Introduction to LR44
The LR44 battery belongs to the category of Alkaline Manganese Batteries, delivering a nominal voltage of 1.5V and a nominal capacity of 120mAh. Operating efficiently within a temperature range of -10°C to 60°C, the LR44 is characterized by its lightweight design, weighing 2 grams. This battery finds extensive use in devices like calculators, watches, digital thermometers, and various electronic gadgets. Despite its moderate lifespan of up to two years, the LR44 is valued for its flat shape convenience, environmental friendliness, and compatibility with an array of applications.

Introduction to 357
The 357 battery is a Silver Oxide cell with a nominal voltage of 1.55V and a nominal capacity of 150mAh. While specific operating temperature ranges are not specified, the 357 battery is recognized for its higher energy density, longevity, and stability in output voltage. Weighing 2.3 grams, this battery is widely used in precision instruments such as watches, calculators, cameras, and various small electronics. The 357 battery's performance is marked by a more constant voltage output throughout its lifespan, making it suitable for applications demanding a reliable power supply.

LR44 vs 357: Specifications
LR44 battery Specifications
|
Specification |
LR44 Battery |
|
Battery Type |
Alkaline Manganese Batteries |
|
Nominal Voltage |
1.5V |
|
Nominal Capacity |
120mAh |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
-10°C to 60°C |
|
Diameter (inch) |
0.457 inch |
|
Diameter (mm) |
11.6mm |
|
Height (inch) |
0.213 inch |
|
Height (mm) |
5.4mm |
|
IEC (JIS) |
LR44 |
|
Mass (oz) |
0.0705 oz |
|
Mass (g) |
2g |
357 battery Specifications
|
Specification |
357 Battery |
|
Battery Type |
Silver Oxide |
|
Nominal Voltage |
1.55V |
|
Nominal Capacity |
150mAh |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
N/A (not specified) |
|
Diameter (inch) |
0.457 inch |
|
Diameter (mm) |
11.6mm |
|
Height (inch) |
0.213 inch |
|
Height (mm) |
5.4mm |
|
IEC (JIS) |
N/A (not specified) |
|
Mass (oz) |
N/A (not specified) |
|
Mass (g) |
2.3g |
LR44 vs 357: Features
Both LR44 and 357 batteries share features such as low self-discharge rates, excellent leakage resistance, and high energy density. However, they differ in their chemical compositions and specific designations, catering to different application requirements.
LR44 Battery Features:
- Chemical Composition: Alkaline (Manganese Dioxide and Zinc)
- Designation: IEC LR44
- Nominal Voltage: 1.5 Volts
- Typical Capacity: 120mAh
- Cost Performance: Achieved through the use of manganese dioxide as a cathode material.
- Discharge Characteristics: Excellent stable discharge and high-drain pulse discharge capabilities.
- Leakage Resistance: Murata-unique sealing structure and special sealing-material treatment provide excellent leakage resistance.
- Battery Type: Alkaline with high energy density and reliable performance.
357 Battery Features:
- Chemical Composition: Silver Oxide (Zn/Ag2O)
- Designation: ANSI-1131SO, IEC-SR44
- Nominal Voltage: 1.55 Volts
- Typical Capacity: 195mAh
- Capacity Test: 6.8K ohm continuous drain at 21°C
- Weight: 2.3 grams
- Volume: 0.57 cubic centimeters
- Impedance (40 Hz): 2 to 8 ohms
- High Energy Density: Delivers more power than alkaline batteries.
- Longevity: Exceptional longevity due to silver oxide chemistry.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: Maintains charge for a long time when not in use.
- Leakage Resistance: Exhibits excellent leakage resistance.
- Battery Type: Silver Oxide with high energy density and long shelf life.
LR44 vs 357: Longevity
The operational lifespan of an LR44 battery is determined by the particular device it powers and the frequency of usage. Typically, an LR44 battery demonstrates a duration of approximately two years in applications characterized by low power consumption.
In contrast, 357 batteries generally provide an extended operational lifespan compared to LR44 batteries. In specific devices, they have the capability to endure for up to five years, making them a preferred choice for applications with intermittent usage patterns.
|
Battery Type |
Operational Lifespan |
Usage Patterns |
|
LR44 |
Up to 2 years |
Low power consumption applications |
|
357 |
Up to 5 years |
Preferred for applications with sporadic usage patterns |
LR44 vs 357: Application
LR44 batteries find widespread use in compact electronic devices like calculators, watches, and digital thermometers. Additionally, they are employed in various applications, including medical devices, toys, and games.
357 batteries are commonly utilized in a range of electronic devices, including medical instruments, watches, calculators, cameras, and other small electronics. Their versatile applications make them suitable for devices where reliable power is essential.
LR44 Battery Applications:
- Calculators
- Watches
- Digital thermometers
- Medical devices (such as glucose meters)
- Toys
- Games
- Hearing aids (in some models)
- Laser pointers
- Small LED flashlights
- Keychain remote controls
357 Battery Applications:
- Medical instruments (such as blood pressure monitors)
- Watches
- Calculators
- Cameras
- Hearing aids (in some models)
- Small electronic devices in the automotive industry
- Electronic thermometers
- Blood glucose meters
- Remote controls
- Electronic car keys
LR44 vs 357: Dimension Outline
The following are the diagrams of LR44 and 357 dimension.
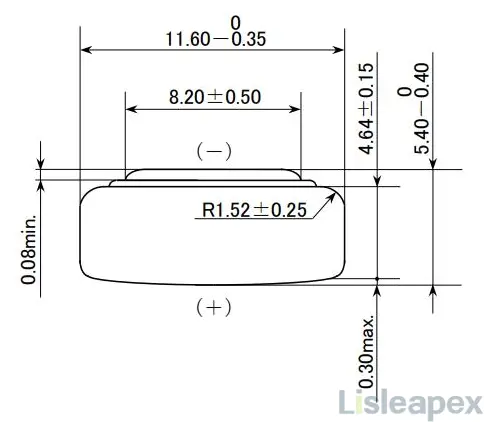
LR44 Battery
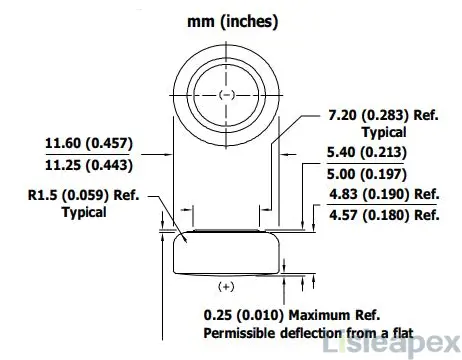
357 Battery
Advantages and Disadvantags of LR44 and 357
Advantages and Disadvantages of LR44
Advantages of LR44:
- Decent Lifespan: LR44 batteries offer a reasonable lifespan, typically providing between 50 and 200 hours of power for various applications.
- Flat Shape Convenience: Despite being flat-shaped, LR44 batteries are user-friendly, with markings indicating positive and negative terminals for easy installation.
- Chemistry Variants: LR44 batteries are available in silver oxide chemistry, although the alkaline variant is more popular due to its affordability and favorable price-to-quality ratio.
- Environmentally Friendly: LR44 batteries are free from toxic materials like mercury or cadmium, contributing to their environmentally friendly nature and easy disposability.
- Lightweight: Being lightweight, LR44 batteries are preferred for applications where weight is a significant consideration.
Disadvantages of LR44:
- Non-Rechargeable: LR44 batteries cannot be recharged once depleted, leading to regular replacements.
- Lower Capacity: Despite having a high energy density, LR44 has a lower capacity compared to other batteries in its class.
- Low Voltage: LR44 operates at a voltage of 1.5V, which is comparatively lower than some other battery types.
- Costly: LR44 batteries are relatively more expensive than certain other battery types, such as zinc carbon and silver oxide batteries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 357
Advantages of 357:
- Long-lasting: The Energizer 357 battery boasts a high energy density, providing extended power for devices with a capacity of approximately 150 mAh.
- Reliable: Manufactured to stringent standards, the Energizer 357 ensures reliability and stability in output voltage, contributing to consistent device operation.
- Wide Compatibility: Available under various model numbers, the 357 battery is a common size used in numerous small electronic devices, offering compatibility across a broad range of applications.
- Convenient Size: Compact and lightweight, the Energizer 357 is easy to carry and store, making it an ideal choice for portable devices.
- Alkaline Chemistry: Utilizing alkaline chemistry, the 357 battery delivers a longer shelf life and superior performance in high-drain devices compared to other battery types.
Disadvantages of 357:
- Non-Rechargeable: Like LR44, the 357 battery cannot be recharged once depleted.
- Capacity Loss Over Time: The 357 battery may experience a loss of capacity over an extended period.
- Heat Sensitivity: More sensitive to heat compared to LR44.
- Cost: The 357 battery is not as cost-effective as some other battery types.
Conclusion: Main Differences between LR44 and 357
The LR44 and 357 batteries exhibit key differences in their chemistry, voltage characteristics, voltage decay patterns, lifespan, size, and cost. LR44, an alkaline battery, is known for its versatility and relatively high energy density, suitable for various applications. However, its voltage output gradually decreases as it discharges.
In contrast, the 357 battery, utilizing silver oxide chemistry, provides a stable and constant voltage output, making it ideal for precision devices with specific voltage requirements. The 357 battery offers a longer lifespan and slightly shorter size, enhancing compatibility in various applications. Both batteries, while reliable, come with cost considerations and are not as economically advantageous as certain alternatives.
Ultimately, the choice between LR44 and 357 depends on specific device requirements and preferences, balancing factors like energy density, voltage stability, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Chemistry Differences: LR44 (Alkaline) vs 357 (Silver Oxide)
|
Feature |
LR44 (Alkaline) |
357 (Silver Oxide) |
|
Chemistry |
Alkaline chemistry |
Silver oxide chemistry |
|
Performance Characteristics |
|
|
|
Common Applications |
|
|
Voltage: LR44 vs 357 Batteries
|
Feature |
LR44 |
357 |
|
Voltage |
1.5V |
1.55V |
|
Device Compatibility |
|
|
|
Voltage Stability |
|
|
|
Sensitivity to Voltage |
- Some devices may have reliability concerns if voltage falls below a certain threshold |
- Preferred for applications with specific voltage requirements |
|
Energy Density |
|
|
Voltage Decay
|
Feature |
Alkaline LR44 Battery |
Silver Oxide 357 Battery |
|
Voltage Decay Characteristics |
|
- More constant voltage output until end of life (1.2 volts) |
|
Implications |
|
|
Lifespan: LR44 vs 357 Batteries
|
Feature |
Alkaline LR44 Battery |
Silver Oxide 357 Battery |
|
Lifespan Characteristics |
|
|
|
Implications |
|
|
|
Percentage Difference |
- LR44 may require more frequent replacements in high-energy devices |
- 357 offers a significant advantage with potentially 30%-100% longer lifespan |
Size: LR44 (Alkaline) vs 357 (Silver Oxide) Batteries
|
Feature |
Alkaline LR44 Battery |
Silver Oxide 357 Battery |
|
Size Characteristics |
- Dimensions: 5.4mm diameter, 11.6mm height |
- Dimensions: 5.4mm diameter, 9.5mm-9.6mm height |
|
Implications |
|
|
Cost
|
Feature |
LR44 |
357 |
|
Cost Consideration |
|
|
Conclusion (Comparison Table):
|
Criteria |
LR44 (Alkaline) |
357 (Silver Oxide) |
|
Chemistry |
Alkaline |
Silver Oxide |
|
Voltage |
1.5V |
1.55V |
|
Voltage Decay |
Gradual and linear decline |
More constant until the end (1.2V) |
|
Lifespan |
Moderate, 110-130 mAh |
Longer, 150-200 mAh or more, depending on discharge |
|
Size |
5.4mm diameter, 11.6mm height |
5.4mm diameter, 9.5mm-9.6mm height |
|
Cost |
Not as cost-effective as some alternatives |
Not as cost-effective as some alternatives |
Are LR44 and 357 cells interchangeable?
The interchangeability of LR44 and 357 cells depends on the specific device's voltage requirements. While both batteries share the same size, their chemical compositions and voltage characteristics differ. The LR44, being an alkaline battery, exhibits a gradual voltage decrease throughout its discharge, while the 357 silver oxide battery maintains a constant voltage near 1.55 volts until nearing depletion.
In many general-purpose applications, LR44 and 357 batteries are considered interchangeable. However, devices that demand a consistent voltage, such as precise calipers and certain watches, may benefit from the 357's stable voltage performance. The 357's higher usable capacity is advantageous for devices with elevated energy demands.
Despite their physical compatibility, it's essential to note that the 357 silver oxide battery outperforms the LR44 in terms of voltage stability and overall performance. For devices designed for the 357's higher voltage and capacity, automatic interchangeability is not recommended. For optimal results, especially in devices like the Insulin pump MiniMed 507C, where long life and steady power output are crucial, it is advisable to use the 357 silver oxide battery instead of the LR44, even if the latter is less expensive.
LR44 Alternative Part
Here are several alternative batteries that can serve as replacements for LR44, each with its own characteristics:
|
Alternative Battery |
Type |
Voltage |
Lifespan |
Remarks |
|
Silver Oxide |
1.55V |
Longer than LR44 |
Similar size and shape, slightly higher voltage, and extended lifespan. |
|
|
357/303 |
Silver Oxide |
1.5V |
Longer than LR44 |
Commonly used, same voltage as LR44 but higher capacity for extended usage. |
|
A76 |
Alkaline |
1.5V |
Similar to LR44 |
Slightly larger, equivalent voltage and capacity, potential for longer life. |
|
AG13 |
Alkaline |
1.5V |
Slightly lower capacity |
Similar size and voltage, may be suitable for certain devices requiring LR44. |
357 Alternative Part
|
Alternative Battery |
Type |
Voltage |
Lifespan |
Remarks |
|
SR44 |
Silver Oxide |
1.55V |
Longer than 357 |
Similar size and shape, slightly higher voltage, and extended lifespan. |
|
LR44 |
Alkaline Manganese |
1.5V |
Similar to 357 |
Interchangeable in certain devices, similar size, and voltage. |
|
A76 |
Alkaline |
1.5V |
Similar to 357 |
Slightly larger, equivalent voltage and capacity, potential for longer life. |
|
AG13 |
Alkaline |
1.5V |
Slightly lower capacity |
Similar size and voltage, may be suitable for certain devices requiring 357. |
Datasheet
Download LR44 datasheet PDF>>
Download 357 datasheet PDF here>>
FAQ
-
Can LR44 and 357 batteries be disposed of in regular household waste?
It is recommended to dispose of LR44 and 357 batteries at recycling centers or locations that accept household hazardous waste. Many communities have specific recycling programs for batteries.
-
Can LR44 and 357 batteries be used in high-drain devices?
While LR44 and 357 batteries are suitable for low to moderate-drain devices, they may not perform well in high-drain applications due to their relatively small capacity.
-
Can LR44 and 357 batteries be used interchangeably?
LR44 and 357 batteries are not always interchangeable because of differences in chemistry, even though they have the same voltage. It's best to use the battery type recommended by the device manufacturer.
-
Are LR44 and 357 batteries rechargeable?
Typically, LR44 and 357 batteries are not rechargeable. They are considered primary (non-rechargeable) cells. Rechargeable alternatives, like the LIR44 or SR44 rechargeable, may be available for some applications.
-
What is the voltage of LR44 and 357 batteries?
LR44 batteries typically have a voltage of 1.5 volts, while 357 batteries, being silver oxide batteries, also usually have a voltage of 1.5 volts.
-
What are the dimensions of LR44 and 357 batteries?
LR44 and 357 batteries have similar dimensions, but they may vary slightly. The diameter is around 11.6 mm (0.457 inches), and the height is around 5.4 mm (0.213 inches) for both types.
Stay updated with Lisleapex by signing up for the newsletter


 Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
 Submission Failure
Submission Failure